A simple arc-length continuation solving the equation. More...
Go to the source code of this file.
Classes | |
| class | CppNoddy::Example::Arc_problem |
| Define the residual for arc-length continuation of a circle. More... | |
Namespaces | |
| namespace | CppNoddy |
| A collection of OO numerical routines aimed at simple (typical) applied problems in continuum mechanics. | |
| namespace | CppNoddy::Example |
Functions | |
| int | main () |
Detailed Description
A simple arc-length continuation solving the equation.
![\[ x^2 + p^2 = 2\,, \]](form_65.png)
where 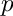
Definition in file ArcCircle.cpp.
Function Documentation
◆ main()
| int main | ( | ) |
Definition at line 39 of file ArcCircle.cpp.
40{
41
42 cout << "\n";
43 cout << "=== ARC: continuation of x^2 + p^2 = 2.0 ============\n";
44 cout << "\n";
45
46 // Instantiate the problem
47 Example::Arc_problem residual_problem;
48 residual_problem.p = 1.0;
49
50 const double tol = 1.e-10;
51 // Scalar Newton iteration problem
52 Newton<double> newton( &residual_problem, 8, tol );
53 newton.set_monitor_det( true );
54
55 // initial guess
56 DenseVector<double> state( 1, 1.1 );
57 // initialise a state for arc length cont.
58 newton.init_arc( state, &residual_problem.p, 0.001, 0.1 );
59
61 for ( int i = 0; i < 100; ++i )
62 {
63 try
64 {
65 try
66 {
67 newton.arclength_solve( state );
68 }
69 catch ( const std::runtime_error &error )
70 {
71 cout << " \033[1;31;48m * FAILED THROUGH EXCEPTION BEING RAISED \033[0m\n";
72 return 1;
73 }
74 }
76 {
77 cout << " Bifurcation detected near x = " << state[ 0 ] << " p = " << residual_problem.p << "\n\n";
78 }
79 if ( abs( pow( state[ 0 ], 2 ) + pow( residual_problem.p, 2 ) - 2.0 ) > tol )
80 {
82 cout << " Error = " << pow( state[ 0 ], 2 ) + pow( residual_problem.p, 2 ) - 2.0 << "\n";
83 }
84 }
85
86 if ( failed )
87 {
88 cout << "\033[1;31;48m * FAILED \033[0m\n";
89 return 1;
90 }
91 else
92 {
93 cout << "\033[1;32;48m * PASSED \033[0m\n";
94 return 0;
95 }
96}
References CppNoddy::Newton< _Type >::arclength_solve(), CppNoddy::ArcLength_base< _Type >::init_arc(), CppNoddy::Example::Arc_problem::p, and CppNoddy::Newton< _Type >::set_monitor_det().
 1.9.5
1.9.5