Solving the Karman rotating-disk equations for the flow above an infinite rotating disk by applying a user-provided Jacobian. More...
Go to the source code of this file.
Classes | |
| class | CppNoddy::Example::Karman_equations |
| Define the Karman equations. More... | |
| class | CppNoddy::Example::Karman_left_BC |
| Define the boundary conditions. More... | |
| class | CppNoddy::Example::Karman_right_BC |
Namespaces | |
| namespace | CppNoddy |
| A collection of OO numerical routines aimed at simple (typical) applied problems in continuum mechanics. | |
| namespace | CppNoddy::Example |
Enumerations | |
| enum | { U , Ud , V , W , Wd } |
Functions | |
| int | main () |
Detailed Description
Solving the Karman rotating-disk equations for the flow above an infinite rotating disk by applying a user-provided Jacobian.
![\[ U''(y) = U^2(y) + V(y)U'(y) - W^2(y) \]](form_92.png)
![\[ W''(y) = 2U(y)W(y) + V(y)W'(y) \]](form_93.png)
![\[ 2U(y) + V'(y) = 0 \]](form_94.png)
with boundary conditions 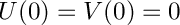
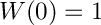
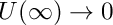
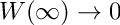
Definition in file BVPKarmanJacobian.cpp.
Enumeration Type Documentation
◆ anonymous enum
| anonymous enum |
Function Documentation
◆ main()
| int main | ( | ) |
Definition at line 99 of file BVPKarmanJacobian.cpp.
100{
101 cout << "\n";
102 cout << "=== BVP: Karman equations with analytic Jacobian ====\n";
103 cout << "\n";
104
105 Example::Karman_equations problem;
106 Example::Karman_left_BC BC_left;
107 Example::Karman_right_BC BC_right;
108
109 // domain for the ODE problem
110 double left = 0.0;
111 double right = 20.0;
112 // number of nodal points
113 int N = 801;
114 // mesh
116
117 // pass it to the ode
118 ODE_BVP<double> ode( &problem, nodes, &BC_left, &BC_right );
119
120 // set the solution to the initial guess
121 for ( int i = 0; i < N; ++i )
122 {
123 double y = ode.solution().coord( i );
124 ode.solution()( i, U ) = 0.0;
125 ode.solution()( i, Ud ) = 0.0;
126 ode.solution()( i, V ) = 0.0;
127 ode.solution()( i, W ) = exp( -y );
128 ode.solution()( i, Wd ) = -exp( -y );
129 }
130
131 try
132 {
133 ode.solve2();
134 }
135 catch ( const std::runtime_error &error )
136 {
137 cout << " \033[1;31;48m * FAILED THROUGH EXCEPTION BEING RAISED \033[0m\n";
138 return 1;
139 }
140
141 const double tol( 1.e-4 );
142 // check the BL transpiration vs the known solution
144 {
145 cout << "\033[1;31;48m * FAILED \033[0m\n";
147 return 1;
148 }
149 else
150 {
151 cout << "\033[1;32;48m * PASSED \033[0m\n";
152 return 0;
153 }
154
155}
A templated object for real/complex vector system of first-order ordinary differential equations.
Definition: ODE_BVP.h:37
DenseVector< double > power_node_vector(const double &lower, const double &upper, const std::size_t &N, const double &power)
Return a DENSE vector with the nodal points of a non-uniform mesh distributed between the upper/lower...
Definition: Utility.cpp:123
References CppNoddy::Utility::power_node_vector(), CppNoddy::ODE_BVP< _Type, _Xtype >::solution(), CppNoddy::ODE_BVP< _Type, _Xtype >::solve2(), U, Ud, V, W, and Wd.
 1.9.5
1.9.5